An Introduction to Cancer Biology Diagrams
An Introduction to Cancer Biology Diagrams The "Cell Cycle Regulators and Cancer" view explains the protein regulators, their roles in cell cycle progression, and how mutated versions can lead to cancer. This view may be more appropriate for AP/IB Biology and introductory college biology. CELL CYCLE AND CANCER. In cancer, there are fundamental alterations in the genetic control of cell division, resulting in an unrestrained cell proliferation. Mutations mainly occur in two classes of genes: proto‐oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes. In normal cells, the products of proto‐oncogenes act at different levels along the pathways

Most cells in the body go through a cycle of life in which their genetic information is retained, fixed, and passed down to daughter cells through a highly coordinated and regulated process. However, during this cell cycle, there are many situations where mistakes are made by the cycle or by a regulating system that causes the cell to proliferate uncontrollably, leading to cancer. Somatic

Genetics, Cancer Cell Cycle Phases Biology Diagrams
Cancer is the result of unchecked cell division caused by a breakdown of the mechanisms that regulate the cell cycle. The loss of control begins with a change in the DNA sequence of a gene that codes for one of the regulatory molecules.

In this article we will discuss about the Cell Cycle and Cancer:- 1. Introduction to Cell Cycle 2. Regulation of the Cell Cycle 3. Regulators 4. Growth Factors and the D-Type Cyclins 5. Inhibitors 6. Involvement of Oncogenes and Anti-oncogenes. Contents: Introduction to Cell Cycle Regulation of the Cell Cycle Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Growth Factors and the D-Type Cyclins Inhibitors
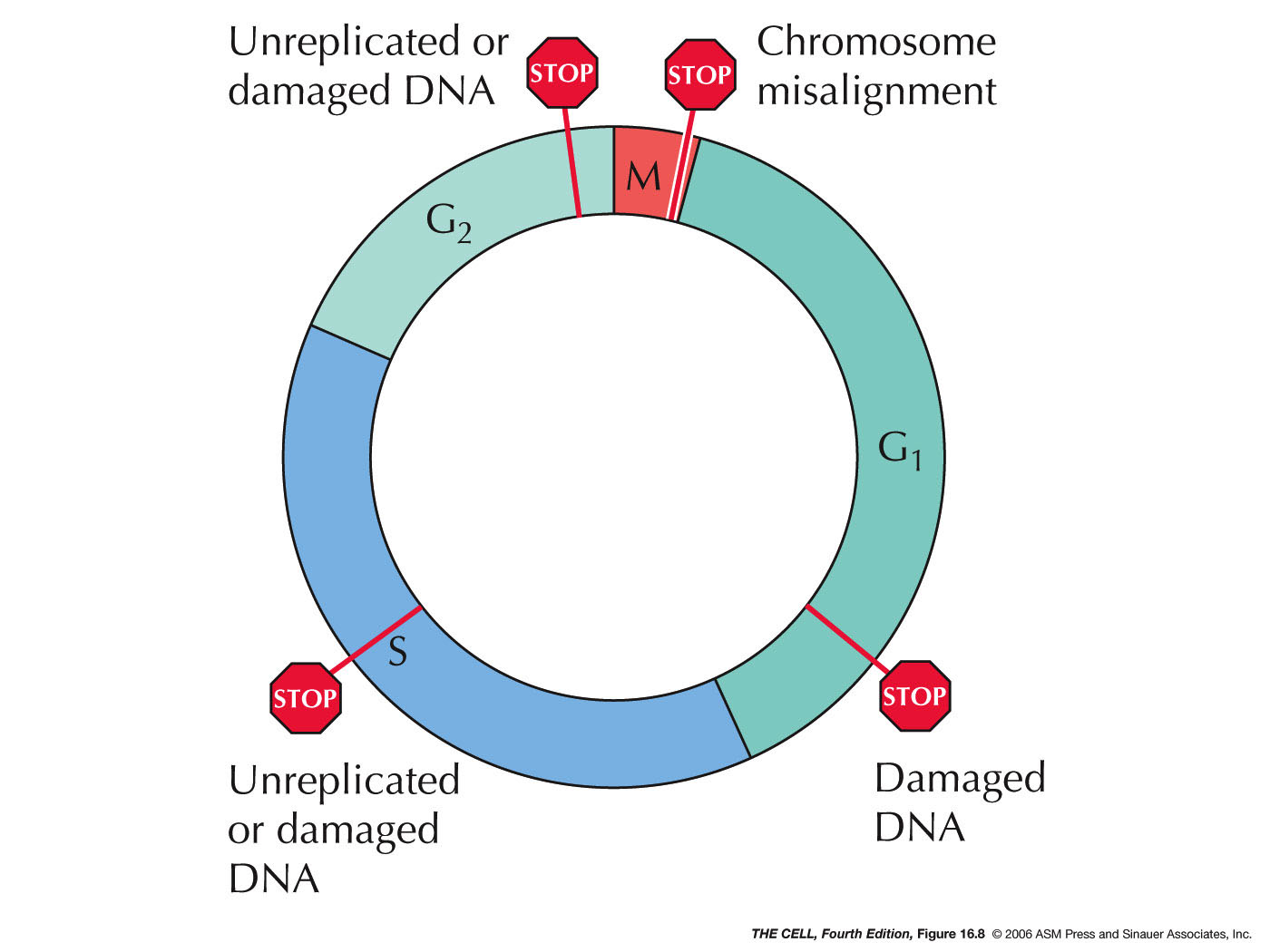
What is the Cell Cycle and How Is It Related to Cancer? Biology Diagrams
Cancer is a group of diseases in which cells divide continuously and excessively. Cell division is tightly regulated by multiple evolutionarily conserved cell cycle control mechanisms, to ensure the production of two genetically identical cells. Cell cycle checkpoints operate as DNA surveillance mec …
