Fungal Cell Diagram Biology Diagrams
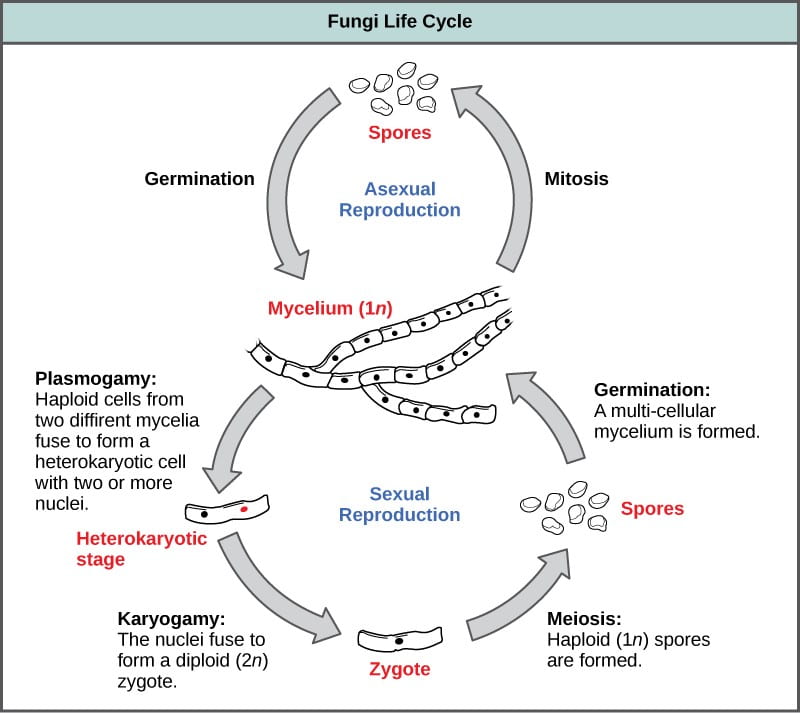
Fungal Cell Diagram Biology Diagrams Additionally, the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus are involved in protein and lipid synthesis, further underscoring the complexity of fungal cells. Fungal Reproduction. Fungi exhibit a diverse array of reproductive strategies that contribute to their adaptability and survival. Reproduction in fungi can be broadly categorized into Unicellular fungi (yeasts) cells form pseudohyphae from individual yeast cells. In contrast to molds, yeasts are unicellular fungi. The budding yeasts reproduce asexually by budding off a smaller daughter cell; the resulting cells may sometimes stick together as a short chain or pseudohypha (Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\)).

Key Terms. glucan: any polysaccharide that is a polymer of glucose; ergosterol: the functional equivalent of cholesterol found in cell membranes of fungi and some protists, as well as, the steroid precursor of vitamin D2; mycelium: the vegetative part of any fungus, consisting of a mass of branching, threadlike hyphae, often underground; hypha: a long, branching, filamentous structure of a 1. Fungi are composed of Eukaryotic cells. Cells with a nucleus and organelles are a common feature of Eukaryotic cells. What is unique about many fungi is that they can maintain two distinct nuclei per cell. Also, some fungi appear to have lost their mitochondria, the organelle responsible for aerobic respiration (using Oxygen to generate ATP). 2.
PDF Structure, Characteristics and Reproduction of Fungi Ii Biology Diagrams
Like plant cells, fungal cells have a thick cell wall. The rigid layers of fungal cell walls contain complex polysaccharides called chitin and glucans.Chitin (N-acetyl-D-glucosamine), also found in the exoskeleton of arthropods such as insects, gives structural strength to the cell walls of fungi.The wall protects the cell from desiccation and some predators. All cells must accurately replicate DNA and partition it to daughter cells. The basic cell cycle machinery is highly conserved among eukaryotes. Most of the mechanisms that control the cell cycle were worked out in fungal cells, taking advantage of their powerful genetics and rapid duplication times …
Unlike plant cells, fungal cells do not have chloroplasts or chlorophyll. Many fungi display bright colors arising from other cellular pigments, ranging from red to green to black. The poisonous Amanita muscaria (fly agaric) is recognizable by its bright red cap with white patches (). Pigments in fungi are associated with the cell wall and play Many of the mechanisms that control the cell cycle were worked out in fungal cells, taking advantage of their powerful genetics and rapid duplication times. The critical insight made by researchers working with fungi in the late 1970s and early 1980s was that distinct cell morphologies could serve as landmarks in-dicating cell cycle stage.
